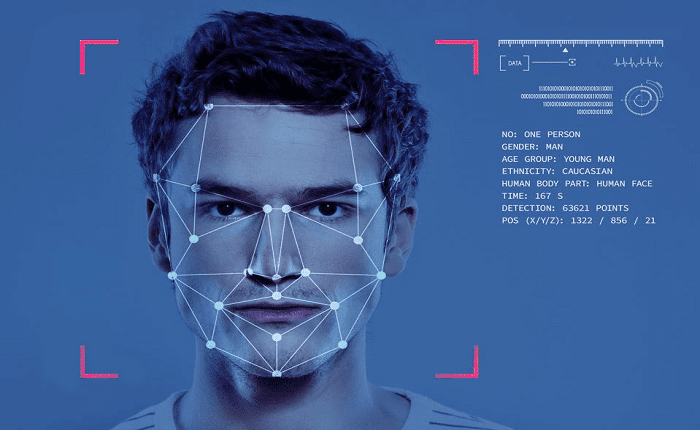
Face identification is the technology that automatically identifies or verifies a person based on facial features. It works by analyzing key characteristics such as the distance between the eyes, the nose’s shape, and the jawline’s contour. Unlike fingerprint scanning or iris recognition, face identification uses visual patterns and machine learning algorithms to map out unique identifiers in a person’s face. This technology can be used in various applications, from unlocking smartphones to securing buildings and monitoring public spaces. The first use of face identification dates back to the early 2000s, but it wasn’t until the advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning models that the accuracy and speed of this technology began to improve. Today, face identification systems can accurately recognize individuals, even under different lighting conditions and at varying angles.
How Does Face Identification Work?
Face identification technology relies on two main processes: face detection and face recognition. The first step is face detection, where the system locates a face within an image or video. This is achieved using algorithms that can differentiate human faces from other objects or backgrounds. Once a face is detected, the system moves on to face recognition. During face recognition, the system analyzes key facial features, such as the distance between the eyes, the nose’s shape, and the mouth’s contours. These measurements are then compared with a stored database of known faces. In some systems, the facial features are converted into mathematical data, which is then matched against a pre-existing data set to confirm or deny an identity.
Types of Face Identification Systems
Several types of face identification systems vary based on their application and the technology they employ. The two primary types are 2D and 3D face identification systems.
2D Face Identification: This is the most common form of identification, using standard cameras to capture images of faces. These systems measure facial features and match them against a stored database. While these systems are cost-effective and widely used, they have some limitations regarding accuracy, especially in challenging lighting conditions or when faces are partially obscured.
3D Face Identifica tion: 3D systems use infrared sensors or special cameras to create a three-dimensional map of a person’s face. This type of identification is more accurate because it accounts for depth and contour, reducing the impact of lighting changes and facial obstructions. However, 3D systems tend to be more expensive and require specialized hardware.
Applications of Face Identification Technology
Face identification has applications in various industries, transforming how businesses and individuals operate. Some common applications include: Security: Face identification is used in security systems to grant or deny access to buildings, rooms, or sensitive areas. Many airports now use face recognition for security checks, making the process quicker and more efficient. Smartphones: Popular smartphones use face identification to unlock devices, ensuring a secure user experience. Apple’s Face ID and similar systems from Android manufacturers have become commonplace. Surveillance: Governments and private organizations use identification for surveillance purposes in public spaces. This can help track criminal activity, monitor crowds, or enhance public safety. Healthcare: Face recognition can help in healthcare by identifying patients, providing accurate medical records, and reducing fraud.
Face Identification and Privacy Concerns
While face identification technology brings numerous benefits, it also raises significant privacy concerns. One of the main issues is the potential for surveillance abuse. With the ability to track individuals without their consent, governments or corporations could use face identification to monitor citizens or customers in ways that compromise their privacy. Additionally, the accuracy of face recognition systems is not foolproof. Mistakes can happen, such as misidentifying a person or falsely denying access. This could lead to security breaches or inconvenience to individuals. Furthermore, the storage and handling of biometric data present another challenge. Hackers who gain access to these data sets could exploit them for identity theft or fraud.
Benefits of Face Identification
The benefits of face identification technology are far-reaching, especially regarding convenience and security. One of the most significant advantages is its ability to provide contactless access. Users no longer need to remember passwords or carry physical keys, making face identification more efficient than traditional identification methods. Moreover, identification is faster and more accurate than other biometric methods, such as fingerprint or iris scanning. As a result, it has become a popular choice for high-security environments like airports and financial institutions. In business settings, identification can enhance customer experience by personalizing interactions based on facial recognition. Retailers can use this technology to recognize returning customers and offer personalized services or discounts.
Face Identification in Law Enforcement
Law enforcement agencies worldwide are increasingly utilizing face identification to assist criminal investigations and prevent crime. Police forces use this technology to identify suspects in real time by matching their facial features against databases of known criminals. Additionally, face identifica tion plays a crucial role in identifying missing persons and locating fugitives. With the proliferation of surveillance cameras in public spaces, law enforcement agencies can now use face recognition to track criminal activities and prevent crimes before they occur. However, the use of face recognition in law enforcement is controversial, particularly regarding its potential to infringe upon civil liberties. Critics argue that it can lead to racial profiling or be used to monitor innocent individuals without cause.
Face Identification in Banking and Finance
Face identification has revolutionized how people access accounts, make payments and verify transactions in the banking and finance sector. Many banks now use face recognition for identity verification during account logins or mobile transactions, reducing the reliance on passwords and PIN codes. This technology has also improved fraud prevention by ensuring only authorized individuals can access financial services. For example, identification can be used to verify customers’ identities during remote banking sessions or while making high-value transactions. As financial institutions continue to embrace face recognition, the technology is expected to reduce fraud rates and streamline financial processes, creating a safer and more efficient environment for both businesses and customers.
The Future of Face Identification Technology
The future of face identification looks promising, with advancements in AI and machine learning driving accuracy, speed, and efficiency improvements. Emerging trends suggest that identification will continue to play a significant role in personal security, healthcare, and customer service, among other industries. One development area is integrating face recognition with other biometric systems, such as voice or fingerprint recognition. This will allow for multi-factor authentication, further enhancing security measures. Face identification technology is also expected to become even more sophisticated, with systems capable of identifying people in crowds or through video footage. However, the future of face recognition will also involve addressing the ethical and privacy concerns associated with the technology. As regulations evolve, developers and companies must work to ensure that identification is used responsibly and transparently.
Challenges Facing Face Identification Technology
Despite its many advantages, face identifica tion technology faces several challenges. The most pressing issue is its accuracy, which lighting, facial expressions, and age can influence. While modern systems are highly accurate, they still have limitations regarding diverse environments and changing conditions.Another challenge is the potential for bias in face recognition systems. Studies have shown that some face identifica tion algorithms are more accurate in identifying lighter-skinned individuals while struggling with darker-skinned faces. This bias raises concerns about fairness and equity, especially in security or law enforcement applications. Finally, as face identification grows, clear regulations to protect users’ rights and privacy are needed. Governments must establish guidelines for the responsible use of face recognition, balancing the need for security with individual freedoms.
Conclusion
Face identification technology is undoubtedly reshaping various industries, enhancing security, improving customer experiences, and streamlining business operations. As we continue to embrace this technology, it is essential to balance the benefits with the ethical concerns and privacy challenges it raises. The key to successful implementation is ensuring that face identifica tion is used responsibly and transparently while addressing issues like accuracy and bias. With the right safeguards, face identification will likely become integral to our everyday lives, improving security and convenience across numerous sectors.
FAQs
What is the difference between face identification and face recognition? Face identification refers to the process of verifying or identifying a person based on facial features, while face recognition involves matching these features with a stored database to confirm identity.
How accurate is face identification technology? Face identification accuracy depends on factors such as lighting, camera quality, and facial expressions. Modern systems are highly accurate but can still experience challenges in certain conditions.
Can face identification be fooled by a photo or video? Advanced face identification systems can detect spoofing attempts using photos or videos by analyzing depth and heat signatures, making it harder to deceive the system.
What are the privacy concerns with face identification? Privacy concerns include the potential for unauthorized surveillance, misuse of biometric data, and the lack of transparency in how data is stored and used by companies and governments.
Is identification safe for online transactions? Yes, face identifica tion enhances security for online transactions by reducing the risk of unauthorized access. However, it’s important to ensure that the system used is reliable and secure.